![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
 |
|
|
|
|
Cellufine Phenyl en Butyl
For purification of proteins and macromolecules.
Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) is a method which separates proteins on the basis of their differential interactions with a mildly hydrophobic surface.
HIC media are porous chromatography particles, manufactured from crosslinked cellulose to which either a butyl, phenyl or octyl functionality has been covalently bonded via a short spacer.
Factors which affect hydrophobic interactions include: salt concentrations, temperature, pH, surfactant and organic solvents. Usually the higher the ionic strength (salt concentration) the stronger the hydrophobic bond. Consequently the interaction is enhanced by conditions inverse to that of ion exchange chromatography. HIC is, therefore, an effective complementary tool for separating and purifying substances which are difficult or cannot be separated by ion exchange.
Partial Structure:
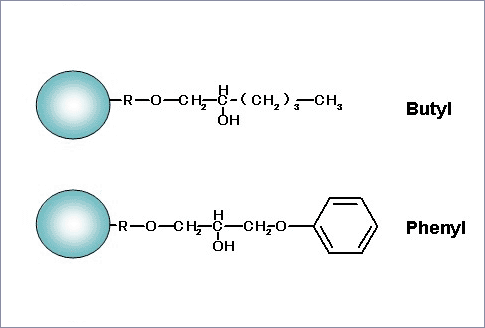
Features:
� Spherical particles exhibiting high mechanical strength
� Butyl, Phenyl, Octyl functionality
� Pre-swollen
� Virtually no shrinkage or swelling
� Stable in organic solvents and surfactants
� Stable coupling chemistry
� Resistant to 0.2 M NaOH
� Autoclavable (121 �C, 20 min)
Benefits:
� High flow rates allowing rapid chromatography and direct scale-up
� Enables optimum selectivity to be obtained
� Easy packing
� Easy large scale operation. No shrinkage at high salt concentrations
� Enables range of solvent systems to be utilized
� Resistant to cleaning and elution conditions
� Sterilizable
� Regulatory support

Hydrophobicity of Matrix:
The degree of hydrophobicity increases in the order of Butyl < Phenyl <
Octyl. In general hydrophobic proteins will be more strongly adsorbed to
Cellufine Octyl than Cellufine Butyl. However, if the protein is too strongly
adsorbed, difficulty may be experienced in elution. The aromatic nature of the
Cellufine Phenyl may, in certain cases, give improved selectivity compared to
either the Butyl or Octyl matrices. Consequently it is difficult to generalize
and each application needs to be evaluated separately to select the optimal
media functionality.
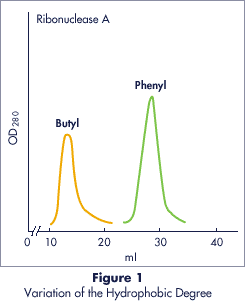
Column : 8.2 x 150 mm
Column Vol. : 8 ml
Buffer : 2.0 � 0.0M
Ammonium Sulfate
in 0.01M phosphate, pH 7.0
Flow Rate : 1.32 ml/min
Sample : 5 mg/3 ml� 100 �l
Figure 1. The retention increases with an increase in the
carbon chain and aromatic structure of the functional group as a result of
stronger hydrophobic interaction.
Flow Properties:
The semi-rigid structure of Cellufine HIC, combined with the spherical bead
shape, gives excellent flow rates with higher operating pressures. Flow rates in
excess of 100 cm/hr are achieved at pressure drops of 1 bar, even in large
diameter process columns.
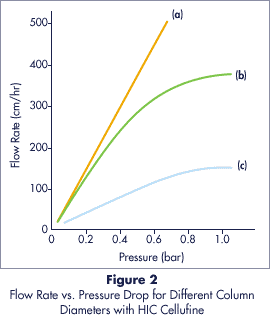
Buffer : 0.01M Phosphate buffer (pH 7.0)
Temperature : 23 �C
Columns : (a) 22 x 300 mm
(Vc = 0.11 liters)
(b) 90 x 200 mm
(Vc = 1.27 liters)
(c) 250 x 250 mm
(Vc = 12.26 liters)
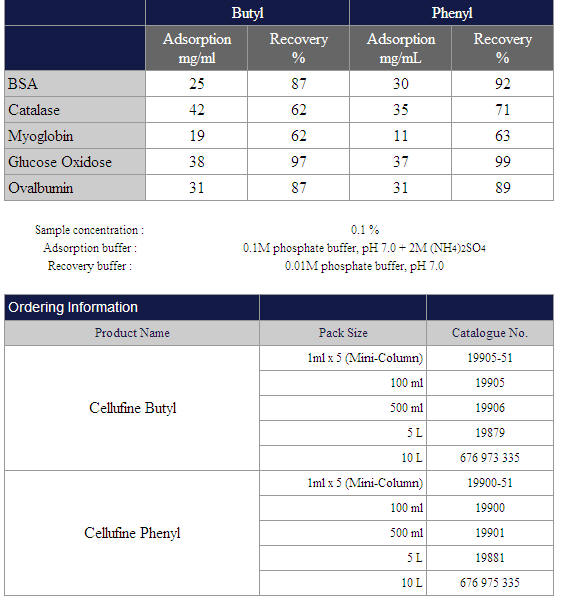
Adsorption Capacity and Recovery Ratio:
|
Send mail to [email protected] with questions or comments about this web site.Copyright � 2009 GENTAUR Last modified: 03/02/10 |